Mobile Application Framework enables you to create an application that can house different types of content that runs on mobile devices powered by Apple iOS platforms or Android devices. This section of the tutorial walks you through configuring your environment so that you can develop and test MAF applications using JDeveloper and an Android environment. In this section you configure, build, and test a small application using the Android environment and emulator. Although we are configuring the environment to use an emulator, you can also deploy to an actual Android device.
This tutorial is written for those who want to work with Android on a PC environment. You may also work with Android emulators in a Apple environment and these instructions are basically the same with some minor variations. The images below show you what your simulator will look like when you successfully complete the tutorial.

This tutorial is written for those who want to work with Android on a PC environment. You may also work with Android emulators in a Apple environment and these instructions are basically the same with some minor variations. The images below show you what your simulator will look like when you successfully complete the tutorial.


- Download and install the Android Stand-alone SDK Tools from http://developer.android.com/sdk/installing/index.html.
You will need to accept the terms and conditions before you download the SDK.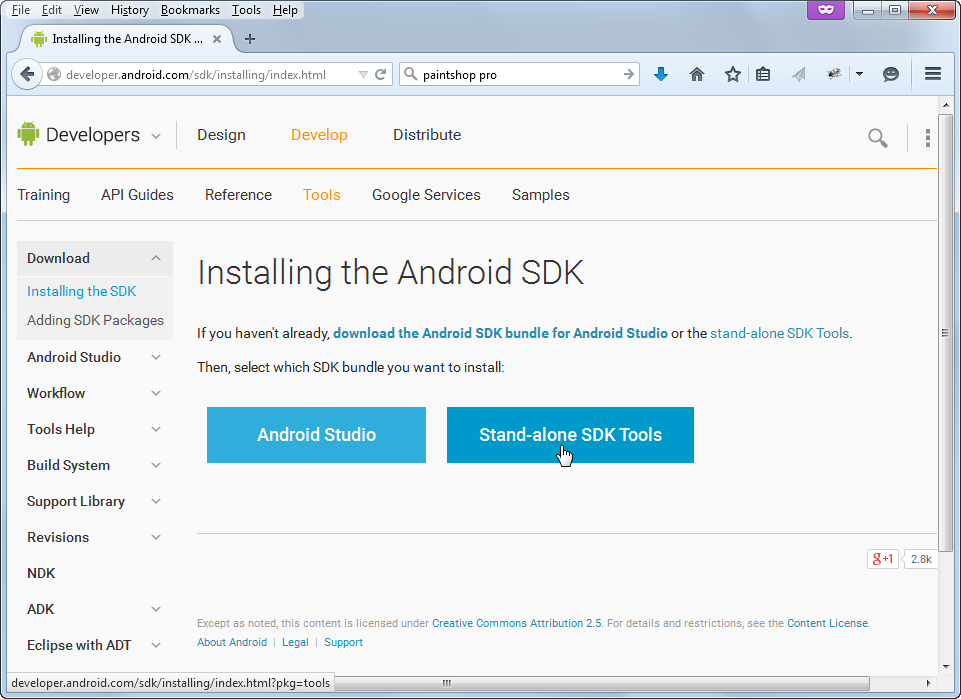
- Run the installer_r24.0.2-windows.exe to install the Android Stand-alone SDK Tools. In the process of installing you can select where the files for the SDK should be placed. Below is what was used for this tutorial.
(At the time of writing this tutorial, this was the name of the file. It may differ at later dates.)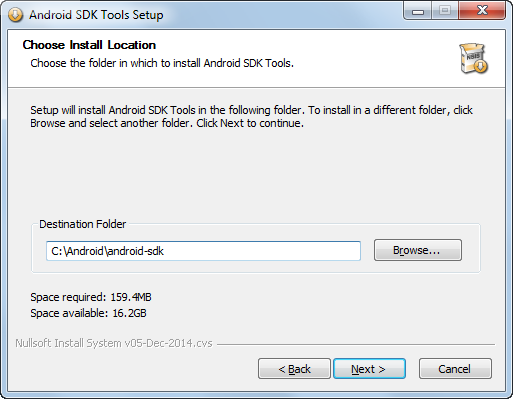
- If you did not select the option to start SDK Manager at the end of the installation, find and double-click the SDK Manager.exe application. The Android SDK Manager is invoked. The Manager is what is used to install all the packages and emulators you use.
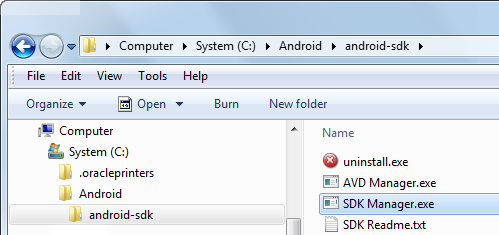
- By default, the Android SDK Tools are installed. Select and install the Android SDK Platform-tools and the Android SDK Build-tools. You will need to accept the software terms to install the packages.
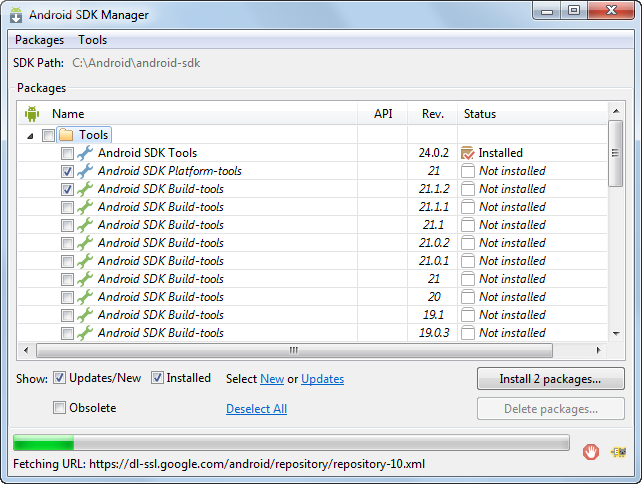
- Select and install the Android 5.0.1 (API 21) components.
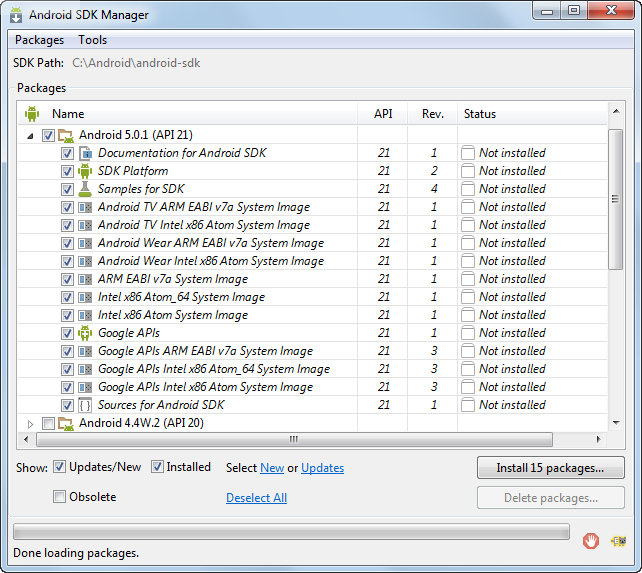
- You also need to download and install some extra packages. Scroll toward the bottom of the SDK Manager, and expand the Extras node.
Select and install the Android Support Repository and Android Support Library packages.
Select and install the Google Cloud Messaging for Android Library package. To see this option you must first select the Obsolete check box at the bottom of the window.
Select and install the Google Repository and Google USB Driver packages.
Select and install the Intel x86 Emulator Accelerator (HAXM) Installer package for the emulator (unless it is already installed).
When you are done, the following packages should be installed: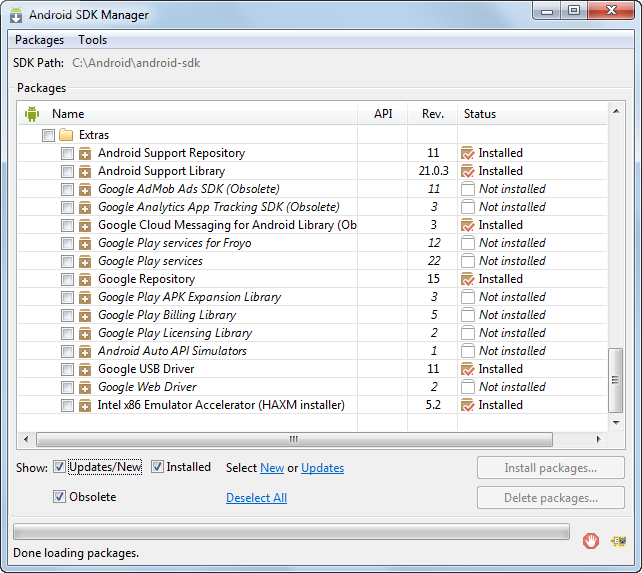
- To use the Intel x86 Emulator Accelerator, once downloaded, you then must then install the drivers.
To install the Intel HAXM executable, search your hard drive for IntelHaxm.exe.
Navigate to Windows Explorer and locate the <android_home>\android-sdk\extras\intel\Hardware_Accelerated_Execution_Manager\intelhaxm-android.exe file. Double click it and you can use the defaults while it installs.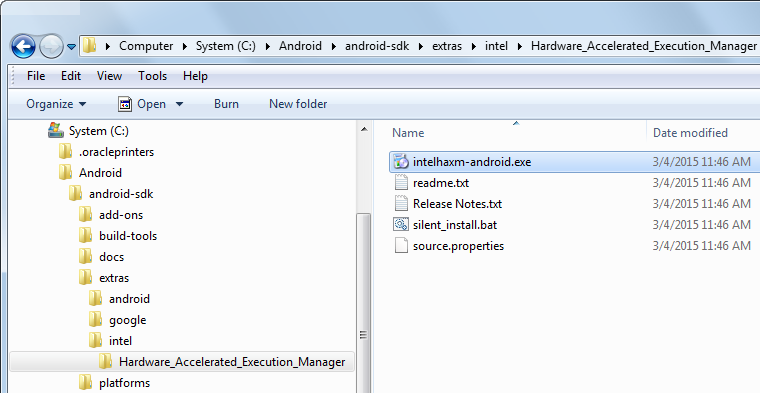
- You will need to have installed JDeveloper Studio Edition (version 12.1.3). You can download JDeveloper from the Oracle JDeveloper 12c home page. Once there, click the Downloads tab to see the JDeveloper download.
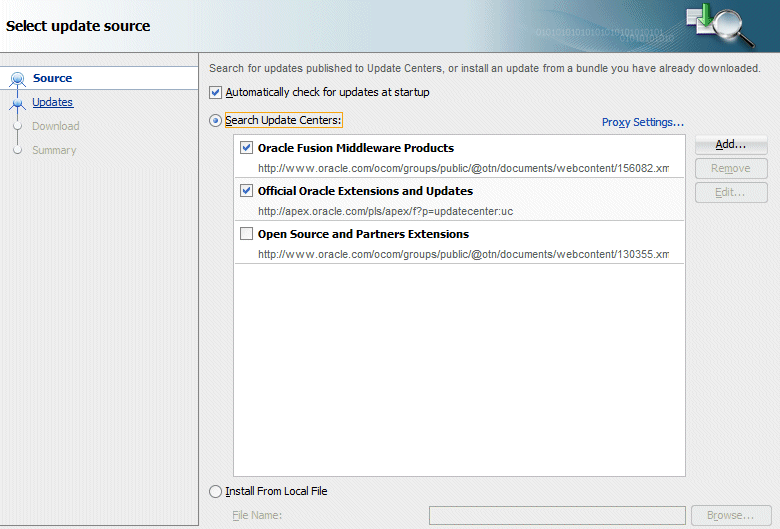
- Install the MAF extension by using the JDeveloper Update Center. Start JDeveloper, and then select the menu item Help - Check for Updates.
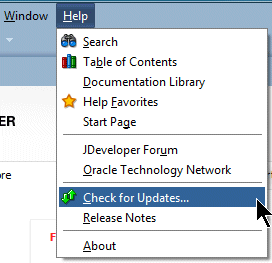
- Click Next at the Welcome dialog.
- Ensure the Search Update Center radio button is selected and click Next.
- In the Available Updates select the check box for the Mobile Application Framework extension.
Then click Next.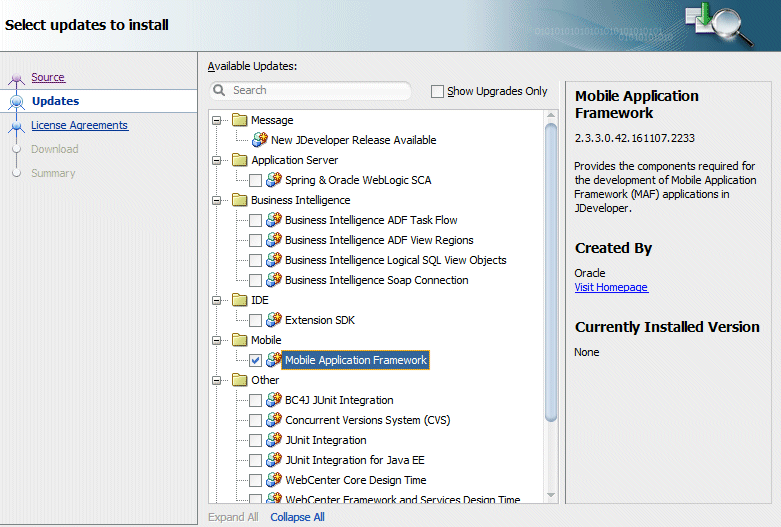
- Accept the licensing agreements by clicking I Agree.
Then, click Next and the download will start. Once the completes, click Next.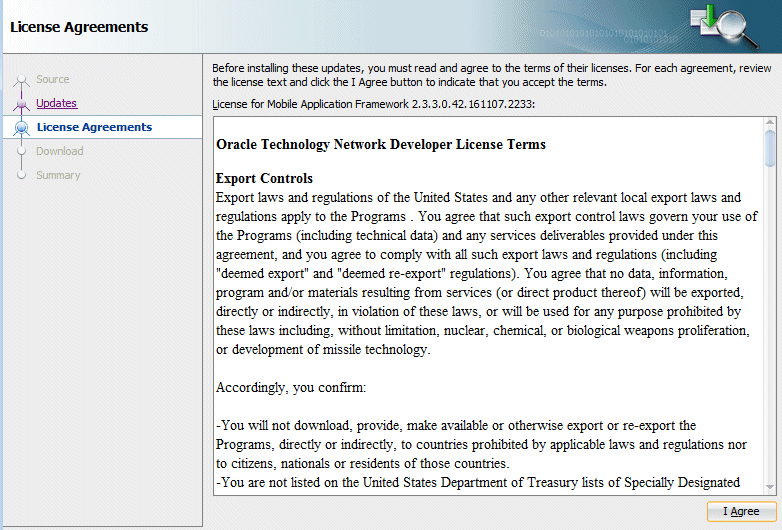
- The download of the extension starts. When it finishes, click Finish.
JDeveloper needs to restart. Click Yes to shut down and restart JDeveloper.
Might take a minute or two, be patient..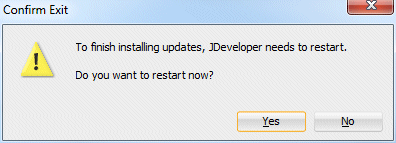
- When JDeveloper is restarted, select Studio Developer (All Features) to be able to use the MAF extension.
When prompted, do not import any preferences from previous versions of JDeveloper. - Next, set the JAVA JDK that MAF will use. You are prompted to specify the location of your installed JAVA 8.
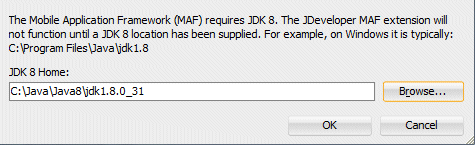
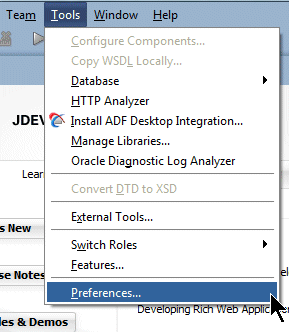
- Then, you must set the SDK that MAF will use. Select the menu item Tools > Preferences.
- On the left side of the Preferences screen, expand the Mobile Application Framework node.
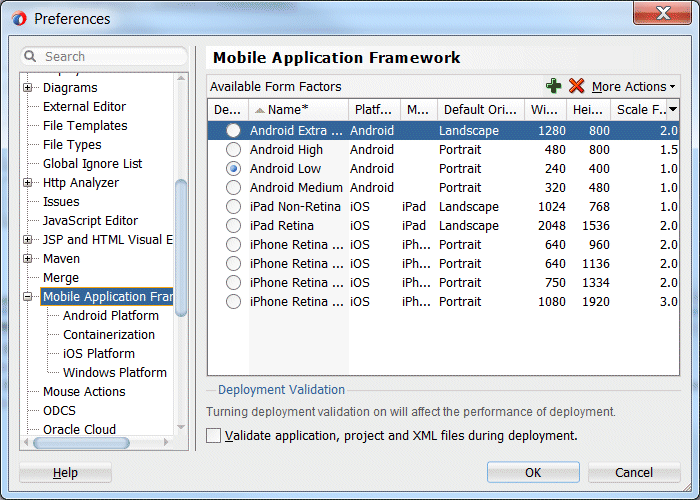
- Then select Android Platform.
- Update all entries with the correct directory locations. If you have installed the SDK to its default location, then you can click on the magnifying glass next to the input list, and navigate to the Android SDK Directory as recommended in the image or your installation location. Do the same for the Android Platform Location and Android Build Tools Location which should point to the directory containing the aapt.exe file.
There is a default password for the debug Key and Keystore. You can ignore those values for now.
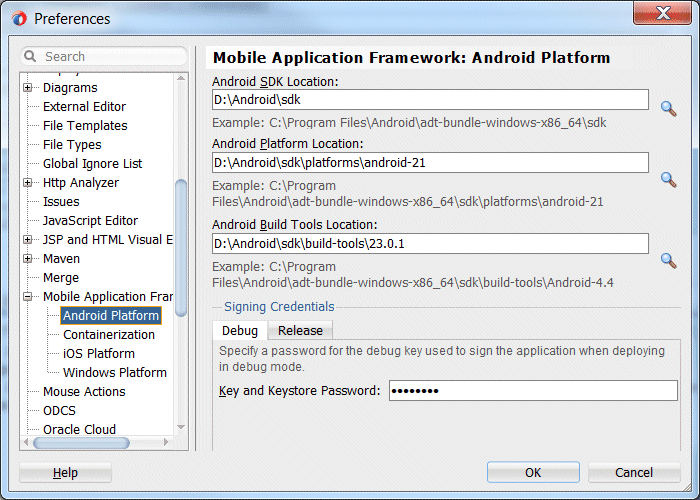
- Click OK to dismiss the Preferences pane.
- Reopen the Android SDK Manager and create and start an Android emulator to use for your mobile deployment.

- In the Android SDK Manager menu bar, select Tools - Manage AVDs...
The Android Virtual Device Manager dialog is displayed.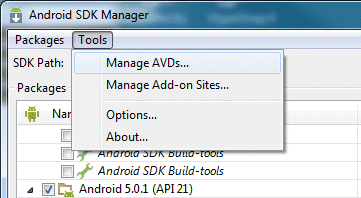
- Click the Create button and specify the following values to the properties.
You may have another emulator already created in the list. Do not use this one, make sure to create a new one according to the specifications below.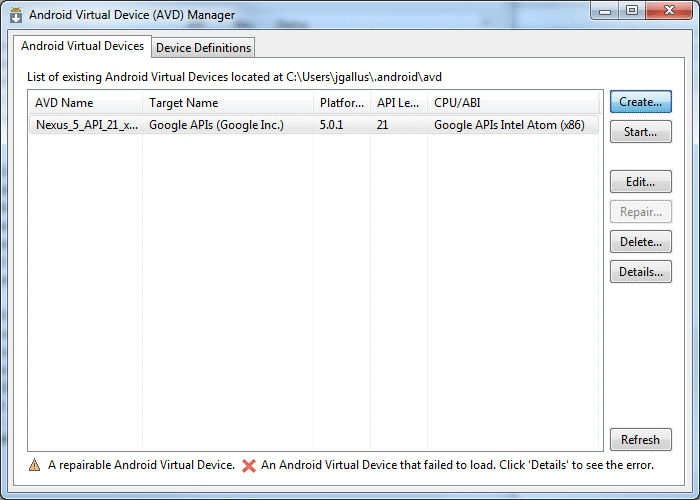
AVD Name = MAF
Device = Nexus 7
Target = Android 5.0.1 - API Level 21
CPU/ABI = Intel Atom (x86_64)
Internal Storage = 200 MiB
Skin = No Skin
Front Camera = Emulated
Back Camera = None
Memory Options Ram = 1024
SD Card = 640 MiB
Use Host GPU = Selected
For the remainder, keep the defaults and click the OK button.
You may choose another device type, keeping in mind that newer devices have greater resource demands and you may run into RAM issues on your own machine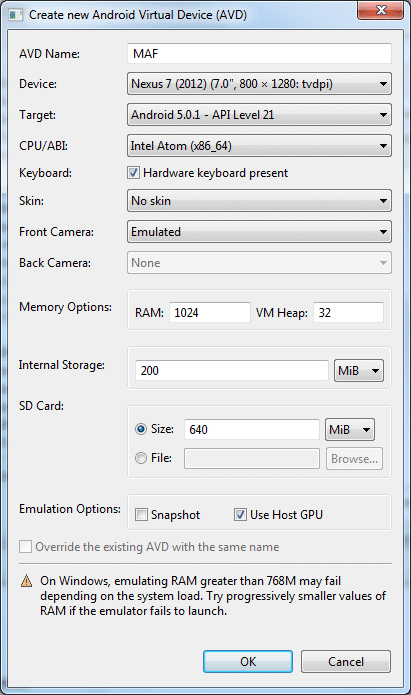
- Select the new AVD and click the Start button.
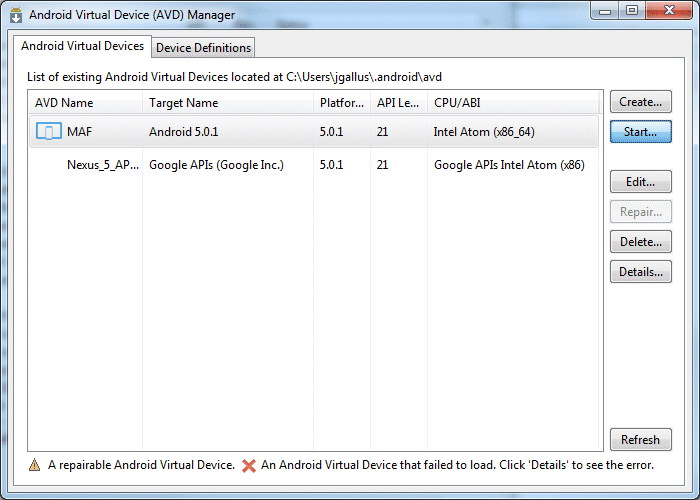
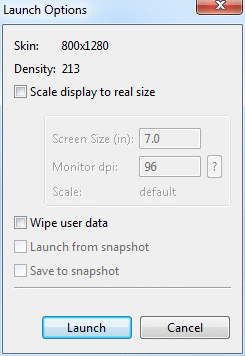
- Accept the default values in the Launch Options pane, and click Launch.
- It may take a few minutes for the emulator to be invoked and start running. Once it's running, you may continue and test your mobile deployment.
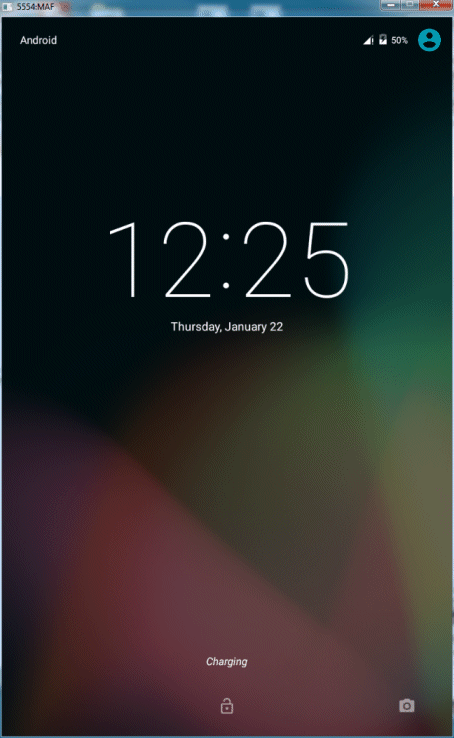
- In this part of the tutorial, you create and deploy a “Hello World” MAF application to the Android emulator. Preparing MAF applications for deployment is primarily comprised of creating platform-specific deployment profiles.
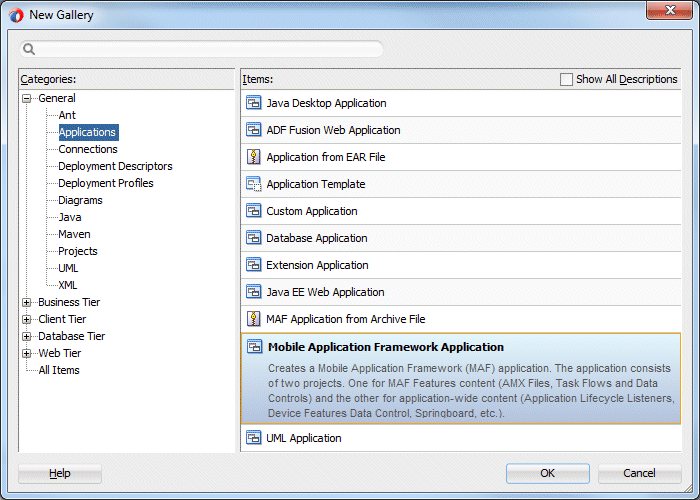
- In the Application Navigator click New Application to start the New Gallery dialog box.
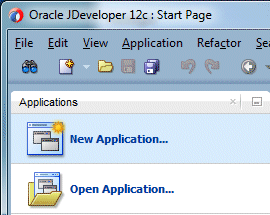
- In the New Gallery expand the General - Applications nodes and select Mobile Application Framework Application and click OK.
In the Name your application page, enter MyMobileApp in the Application Name field, and click Next.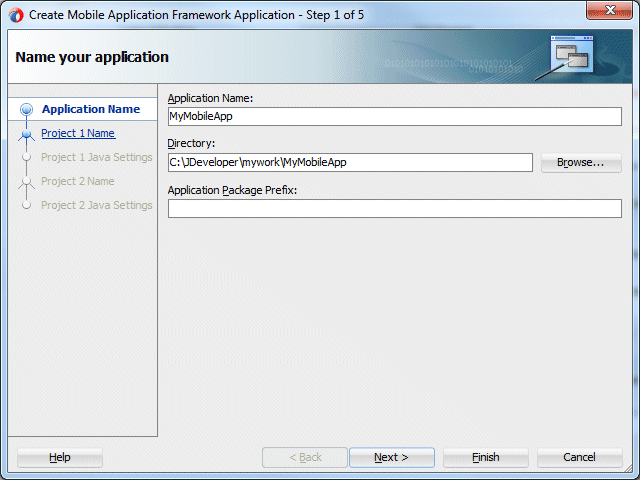
- Examine the Project Features for your first project, the ApplicationController.
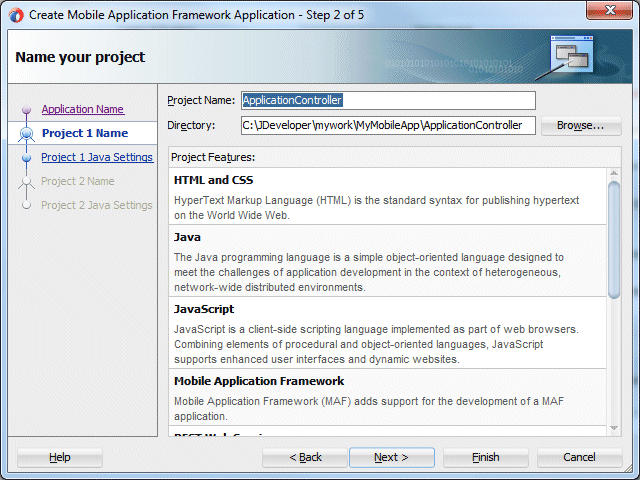
- Click Next twice and in the Name your project page, leave the default project name for the second project ViewController. Examine the Project Features for the ViewController project. Notice that the project uses Mobile Application Framework, HTML and CSS, Java, and JavaScript project features.
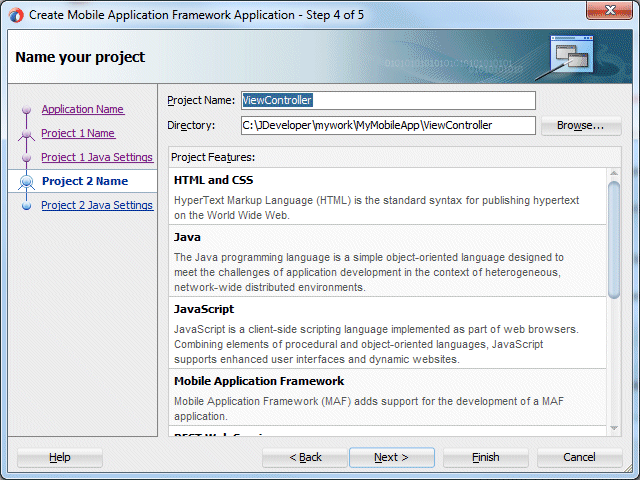
- Click Next and Finish. In the Application Navigator, all the files associated with a new MAF application are viewable.
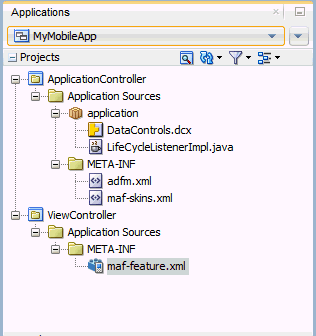 After you complete a MAF Framework application, JDeveloper adds both project and application level artifacts. Among these artifacts is a MAF framework model project and the view-controller project (with the default name, ViewController) that has the MAF framework feature application resources. These resources include the configuration file for applications features, maf-feature.xml. The configuration file is a stub XML descriptor file that enables you to define feature applications that will be seen when the application runs. The maf-feature.xml defines details of each feature - for example, its icon, content type, starting point, etc.
After you complete a MAF Framework application, JDeveloper adds both project and application level artifacts. Among these artifacts is a MAF framework model project and the view-controller project (with the default name, ViewController) that has the MAF framework feature application resources. These resources include the configuration file for applications features, maf-feature.xml. The configuration file is a stub XML descriptor file that enables you to define feature applications that will be seen when the application runs. The maf-feature.xml defines details of each feature - for example, its icon, content type, starting point, etc.
The maf-application.xml file defines the details of the application itself, including reference to features. These feature applications, when packaged into a JAR file known as a Feature Archive file (FAR), provide the reusable content that can be consumed by other MAF applications. One reason for this distinction is to allow developers to create feature archives (which may contain one or more features referenced in the maf-feature.xml), and then create applications by simply pulling in feature archives. Of course each app would only have one maf-application.xml.
A FAR is essentially a self-contained collection of everything that a feature requires, such as icon images, resource bundles, HTML, JavaScript, or other implementation-specific files. The FAR includes a single maf-feature.xml file, which identifies each of the packaged feature applications by a unique ID. You can edit this file to update feature properties. For example, you can specify the content implementation (local or remote HTML files, AMX pages, or a native application written in platform-specific language). You can also control the display of content based on such factors as user roles and privileges, or device properties. A mobile application can reference one FAR, several of them, or none at all. - Right-click on the ViewController project and select New > From Gallery.
In the New Gallery, select Web Tier - HTML and then the HTML Page item. Click OK.
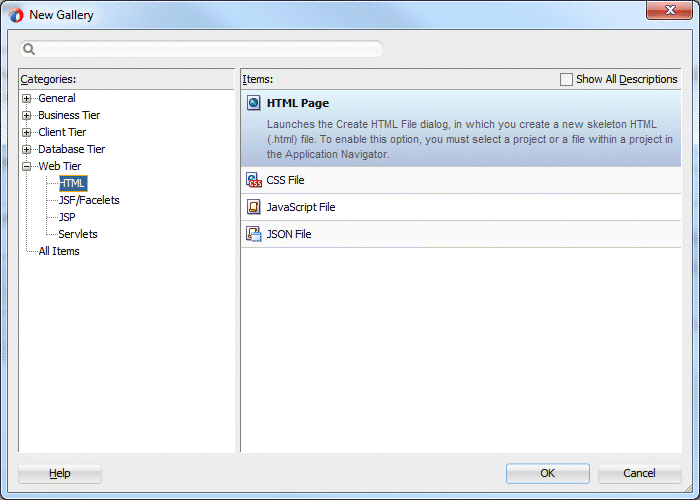
- Accept the default File Name and Directory, then click OK.
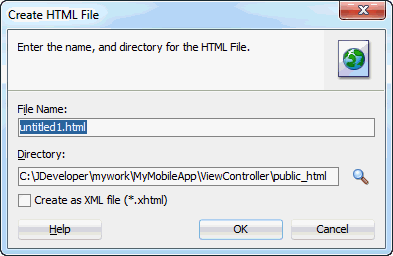
- In the Editor, type the following text "Deployment Successful".
Then in the Properties Window, expand the Style node and set the Font Size to xx-large.
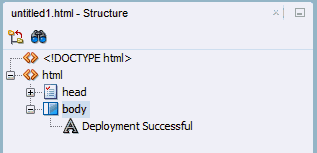
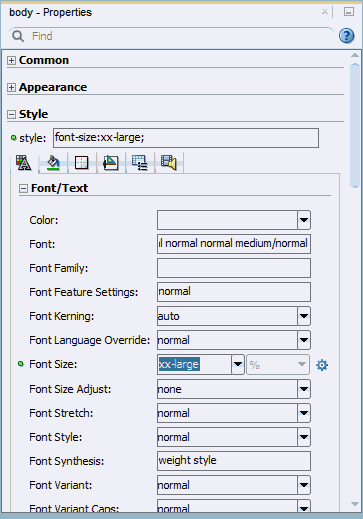
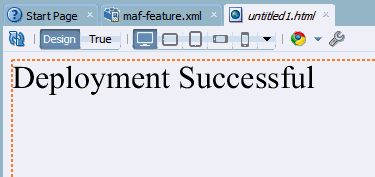
- Save your work.
A deployment profile defines how an application is packaged into the archive that will be deployed to either an iOS or Android platform.
The deployment profile:
- Specifies the format and contents of the archive.
- Lists the source files, deployment descriptors, and other auxiliary files that will be packaged into the archive file.
- Describes the type and name of the archive file to be created.
- Highlights dependency information, platform-specific instructions, and other information.
- In this section, you configure a new feature so the user can access the newly defined local HTML page from the native application container. You will need to perform this task whenever you add pages or task flows to your application.
- In the Application Navigator, expand the ViewController project. Locate and expand the Application Sources folder. Then expand the META-INF folder. You will see the maf-feature.xml file as shown.
- Double click on the maf-feature.xml file to open the Feature editor.
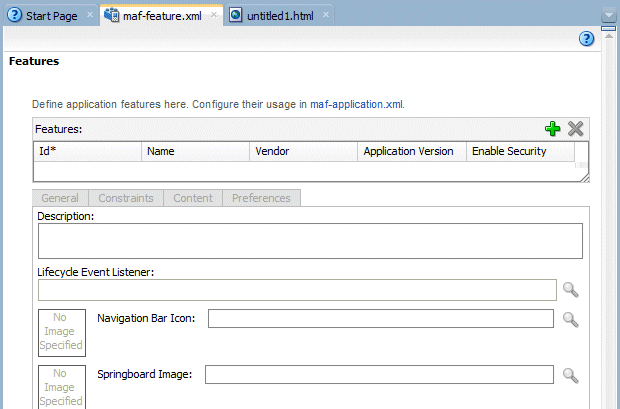
- Add a new feature by clicking the green plus sign on the Features table near top of the editor. If you cannot see the plus sign, scroll the Feature editor to the right (the plus sign is on the far right side of the Feature editor).
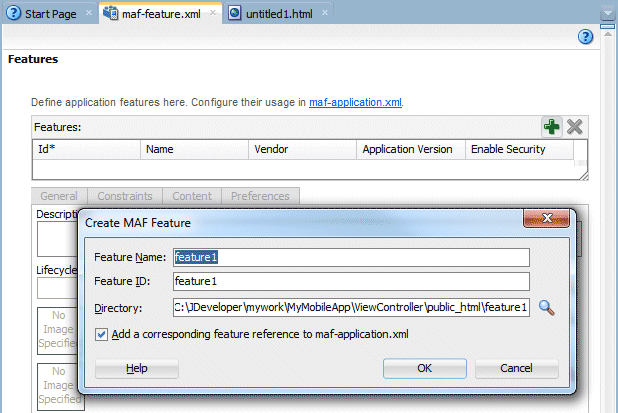
- In the Create MAF Feature dialog, modify the following values:
- Feature Name: Success
- Feature ID: oracle.success
Accept the default directory value, and confirm the Add a corresponding feature reference to maf-application.xml check box is selected, and then click OK.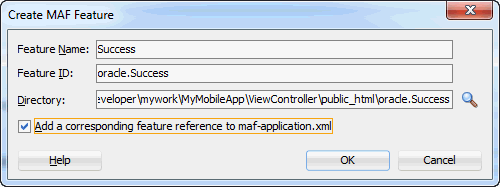
- In the Features table, select the newly created feature oracle.success. Under the Features table, click the Content tab, and locate the Content table. Notice that the content item oracle.Success.1 is created by default.
- Save your work.
- In the Content area, set the Type property is set to Local HTML.
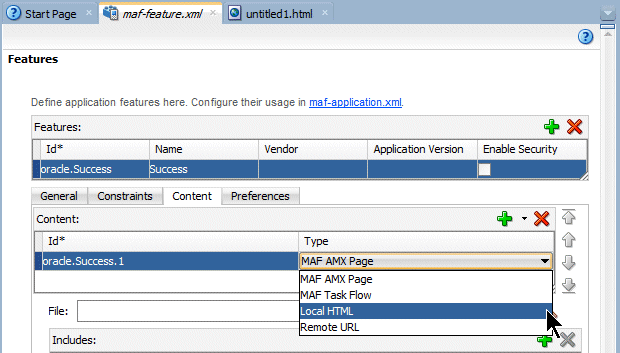
- In the Content section, find the URL text box.
On the right side of the URL text box, click the magnifying glass icon.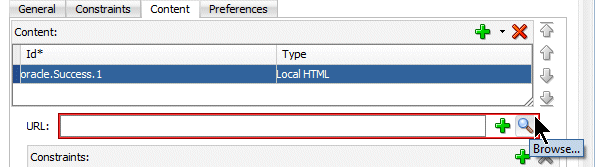
- In the Open window, select the html page you created earlier. In this case, untitled1.html. Then click Open.
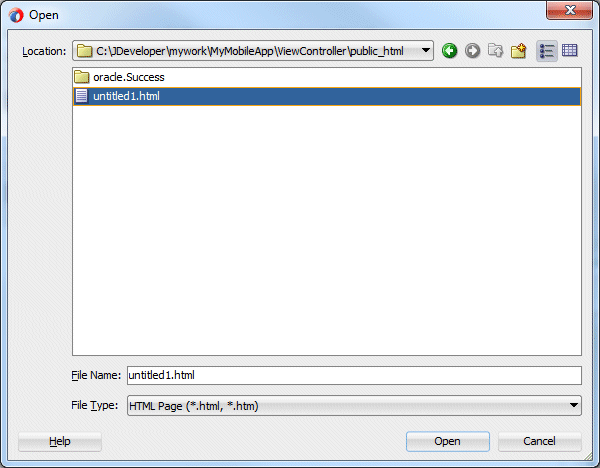
- The resulting definition should look like the image below.
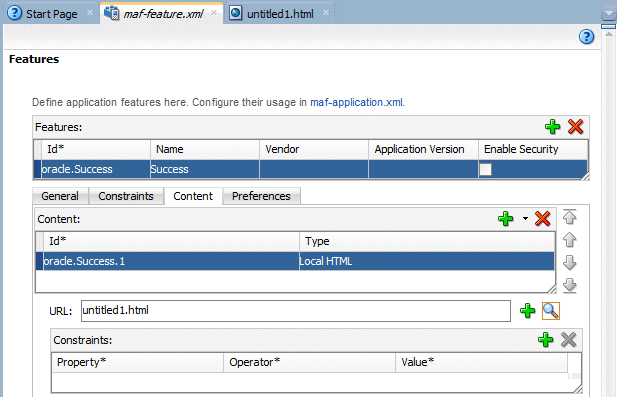
- Save all your work.
- Now that you have an environment installed and have created an application, you're ready to deploy the application to the emulator.
- Confirm your emulator is still running. At the bottom of the emulator, click the Applications icon and all the installed applications will be visible. Keep the emulator open and return to JDeveloper and the MyMobileApp application.
- In the Application menu, select Deploy - New Deployment Profile to start the Create Deployment Profile dialog box.
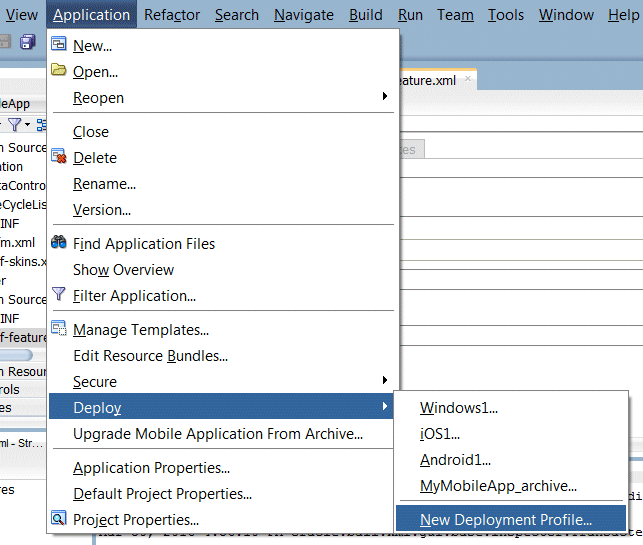
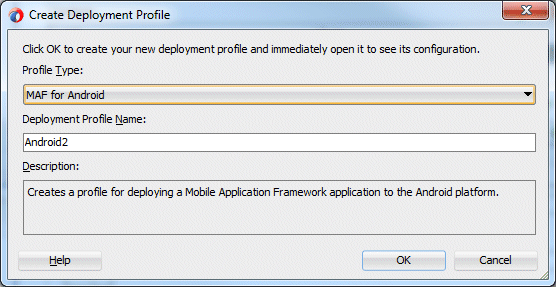
- In the Profile Type drop-down list, ensure MAF for Android is selected. Enter Android2 as the Deployment Profile Name and click OK.
- Select the Android Options node and confirm your values look like the ones below.
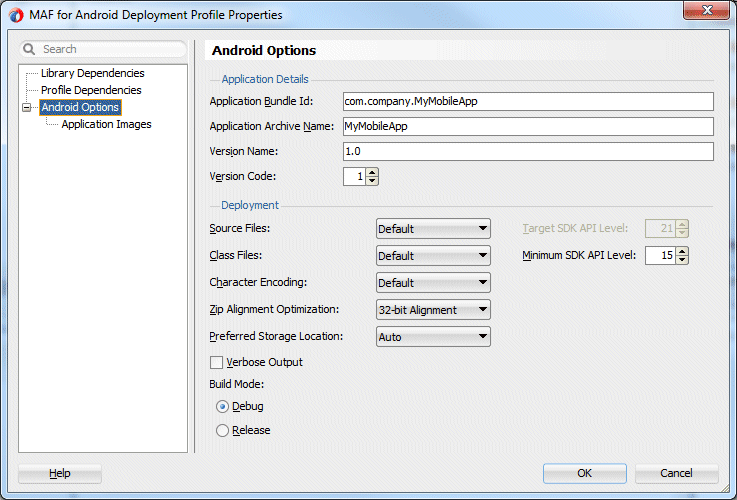
- Click OK, and then save all your work.
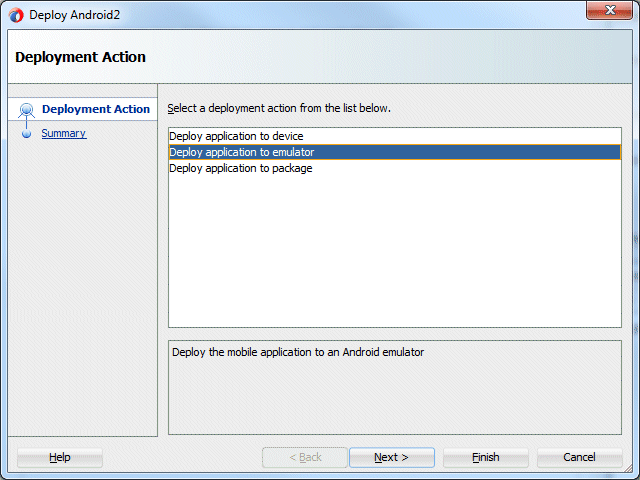
- In the Application menu, select Deploy > Android2...
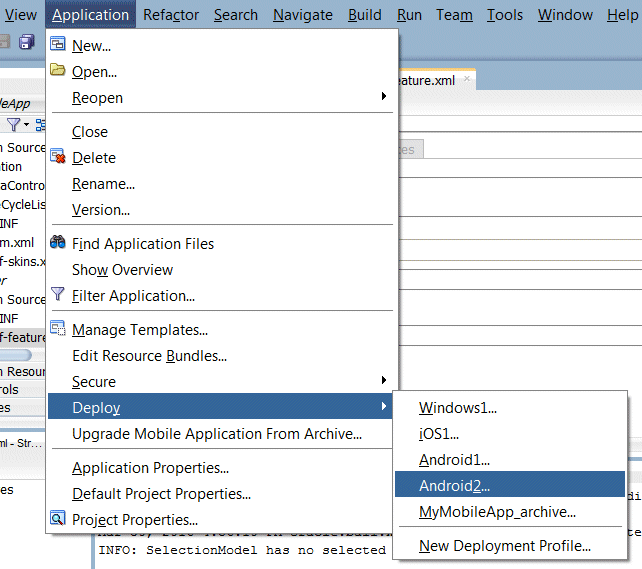
- In the subsequent dialog box, select Deploy application to emulator, and click Finish.
- Watch the Deployment Log window for any errors. If the compilation and deployment process completes as expected, you should see the Deployment Log window as shown below.
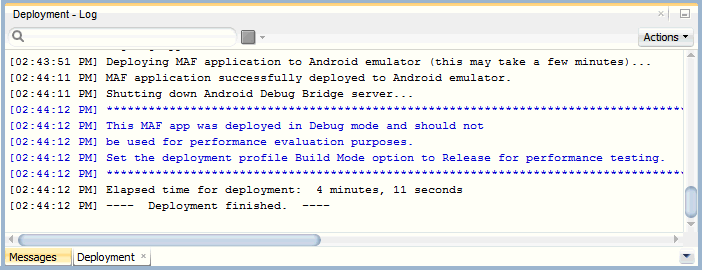
- Navigate back to the emulator.
You should see the MyMobileApp application you have just created and deployed. - Click the MyMobileApp icon to start the application.
- If you are finished, then close the emulator, but remember to restart it before you want to deploy to it again.
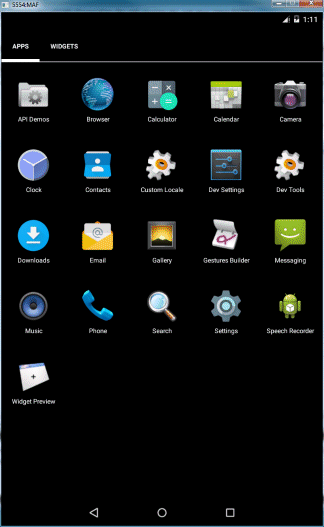

The MyMobileApp application currently contains your HTML page running inside the MAF application.

It's too easier to use the android app for any user, and from 3rd addition to tilling now, its upgrading android features in comprehensive mode. It's really much popular in mid-range devices as compare then, iOS, Microsoft and Blackberry operating systems. Now we can say Android mobile app development has taken higher positions in the Asia Pacific region along with Malaysia, Singapore and India regions.
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing valuable information. Your blogs were helpful
ReplyDeleteAndroid course
When it comes to mobile app development, you should know exactly what you stand to gain. Mobile apps need not be limited to gaming: the Mobile App Developmentbenefits are many, and they could be exactly what you need to boost your business. Taking the first step on the mobile app development journey could just be the early bird investment you need to make your business a success. Mobile apps are growing at an unprecedented rate, and they are becoming the preferred way of doing business for many people.
ReplyDeleteAs more and more business owners turn to a web presence to help grow their business, the need for web and mobile app developmenthas grown too. To make matters more complicated, there are a lot of different factors to take into account when deciding whether to develop your app in-house or to hire a freelance developer or a web and mobile app development house to do it for you.
ReplyDeleteI read your blog it's very nice and very helpful, I learn something new every time from this website, Thanks for sharing this information with us. I am also a blogger i guide people on App and Software Development. You can visit my blog here android app development
ReplyDeleteThe information you have deliver here is really useful to make my knowledge good. Thanks for your heavenly post. It is truly supportive for us and I have accumulated some essential data from this blog. mobile app development company
ReplyDelete